컴포넌트(component)는 리액트에서 앱을 이루는 최소한의 단위로,
특정 코드 뭉치를 다른 부분에 이식하거나 재사용하기 위해 사용하는 코드 블록 단위를 말합니다.
컴포넌트는 파일 단위로 작성한 후, 필요한 위치에서 임포트해 사용할 수 있습니다.
이러한 컴포넌트는 생명 주기(=Life cycle, 라이프 사이클)를 가집니다.
생명 주기 함수 (Life cycle Method)
생명 주기는 컴포넌트의 생성, 변경, 소멸 과정을 뜻합니다. 즉, 페이지에 렌더링되기 전인 준비 과정에서 시작하여 페이지에서 사라질 때까지의 과정을 의미합니다.
각각의 과정마다 특정한 함수(메서드)를 실행하는데, 이 함수들을 생명 주기 함수(라이프 사이클 메서드)라고 합니다.
- 생성 과정
1. render()
render()는 return되는 html 형식의 코드를 화면에 그려주는 함수입니다.
화면 내용이 변경되어야 할 시점에 자동으로 호출됩니다.
import React from 'react';
import './App.css';
import LifecycleEx from './R004_LifecycleEx'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Start React 200!</h1>
<p>CSS 적용하기</p>
<LifecycleEx></LifecycleEx>
</div>
);
}
export default App;App.js
import React, {Component} from 'react';
class R004_LifecycleEx extends Component {
render(){
console.log('3. render Call');
return (
<h2>[THIS IS RENDER FUNCTION ]</h2>
)
}
}
export default R004_LifecycleEx;R004_LifecycleEx.js

<LifecycleEx> 부분에 return 값 [THIS IS RENDER FUNCTION]과 콘솔창에 "3. render Call" 이 올바르게 출력된 것을 볼 수 있습니다. R004에서 작성한 컴포넌트가 잘 이식되었습니다.
2.constructor(props)
constructor(props)함수는 생명주기 함수 중 가장 먼저 실행되며, 처음 한 번만 호출됩니다.
컴포넌트 내부에서 사용되는 변수(state)를 선언하고 부모 객체에서 전달받은 변수(props)를 초기화할 때 사용합니다. super() 함수는 가장 위에 호출해야 합니다.
import React, {Component} from 'react';
class R005_LifecycleEx extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {};
console.log('1. constructor Call');
}
render(){
console.log('3. render Call');
return (
<h2>[THIS IS CONSTRUCTOR FUNCTION ]</h2>
)
}
}
export default R005_LifecycleEx;R005_LifecycleEx.js
App.js 는 1번과 동일합니다.

콘솔 창에 1. constructor Call -> 3. render Call 순서로 출력되는 것을 보면, constructor(props) 함수가 가장 먼저 실행되어 변수를 초기화 함을 알 수 있습니다.
3. static getDerivedStateFormProps(props, state)
getDerivedStateFormProps(props, state) 함수는 constructor() 함수 다음으로 실행됩니다.
컴포넌트가 새로운 props를 받게 됐을 때, state를 변경해줍니다.
참고로 이 메서드는 컴포넌트가 처음 렌더링 되기 전에도 호출 되고, 그 이후 리렌더링 되기 전에도 매번 실행됩니다.
import React from 'react';
import './App.css';
import LifecycleEx from './R006_LifecycleEx'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Start React 200!</h1>
<p>CSS 적용하기</p>
<LifecycleEx
prop_value = 'FromApp.js'
/> //R006.js에 변수 prop_value를 전달
</div>
);
}
export default App;App.js
import React, {Component} from 'react';
class R006_LifecycleEx extends Component {
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state){
console.log('2. getDerivedStateFromProps Call : '+props.prop_value); //props.변수명으로 값을 가져올 수 있음
return {};
}
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {};
console.log('1. constructor Call');
}
render(){
console.log('3. render Call');
return (
<h2>[THIS IS CONSTRUCTOR FUNCTION ]</h2>
)
}
}
export default R006_LifecycleEx;R006_LifecycleEx.js

콘솔 창을 보면 1 -> 2-> 3 순서로 출력되어 함수가 constructor -> getDerivedStateFromProps -> render 순으로 실행 됨을 확인할 수 있습니다. 또한, App.js에서 전달한 prop_value 라는 변수를 props.prop_value로 접근해 값(FromApp.js)도 잘 받아왔습니다.
4. componentDidMount()
componentDidMount() 함수는 작성한 함수들 중 가장 마지막으로 실행됩니다.
render() 함수가 return되는 html 형식의 코드를 화면에 그려준 후 실행되기에, 이벤트 처리, 초기화 등 가장 많이 활용됩니다.
import React, {Component} from 'react';
class R007_LifecycleEx extends Component {
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
console.log('2. getDerivedStateFromProps Call :'+props.prop_value);
return {tmp_state:props.prop_value};
}
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state={};
console.log('1. constructor Call');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('4. componentDidMount Call');
console.log('5. tmp_state : '+this.state.tmp_state);
}
render(){
console.log('3. render Call');
return (
<h2>[THIS IS COMPONENTDIDMOUNT FUNCTION ]</h2>
)
}
}
export default R007_LifecycleEx;R007_LifecycleEx.js
App.js 는 1번과 동일합니다.
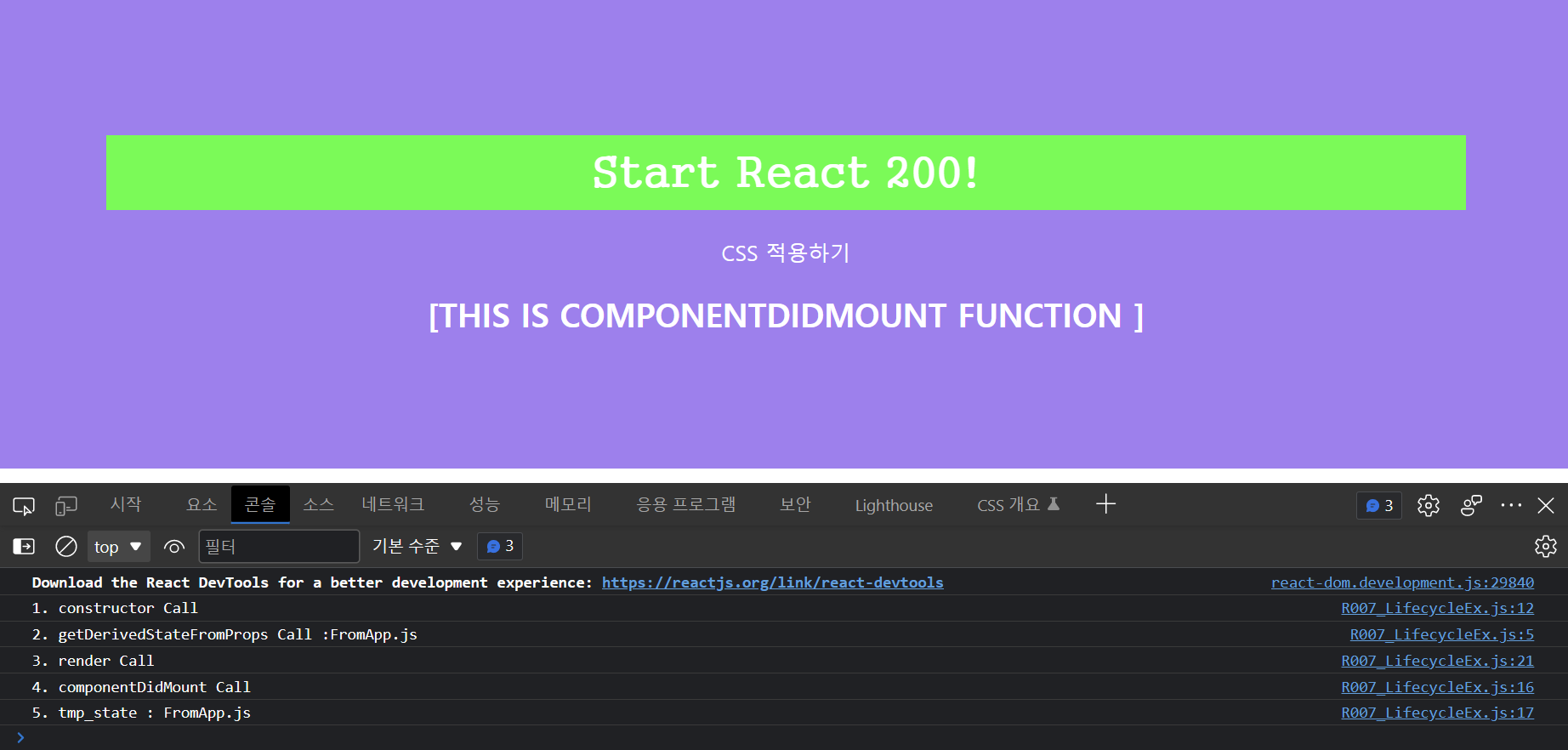
콘솔 창을 보면 함수 실행 순서와 getDerivedStateFromProps 함수에서 변경된 state 값도 잘 받아왔음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
- 변경 과정
5. shouldComponentUpdate()
여기서 변경은 props나 state의 변경을 말합니다.
shouldComponentUpdate() 함수는 boolean 유형의 데이터를 반환하는데, return 값이 true일 경우에 render() 함수를 한 번 더 호출, 재실행합니다.
import React, {Component} from 'react';
class R008_LifecycleEx extends Component {
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
console.log('2. getDerivedStateFromProps Call :'+props.prop_value);
return {tmp_state:props.prop_value};
}
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state={};
console.log('1. constructor Call');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('4. componentDidMount Call');
console.log('5. tmp_state : '+this.state.tmp_state);
this.setState({tmp_state2 : true}); //변수 선언, 초기화 동시 실행
}
shouldComponentUpdate(props, state) {
console.log('6. shouldComponentUpdate Call / tmp_state2 = '+state.tmp_state2);
return state.tmp_state2
}
render(){
console.log('3. render Call');
return (
<h2>[THIS IS shouldComponentUpdate FUNCTION ]</h2>
)
}
}
export default R008_LifecycleEx;R008_LifecycleEx.js
App.js 는 1번과 동일합니다.
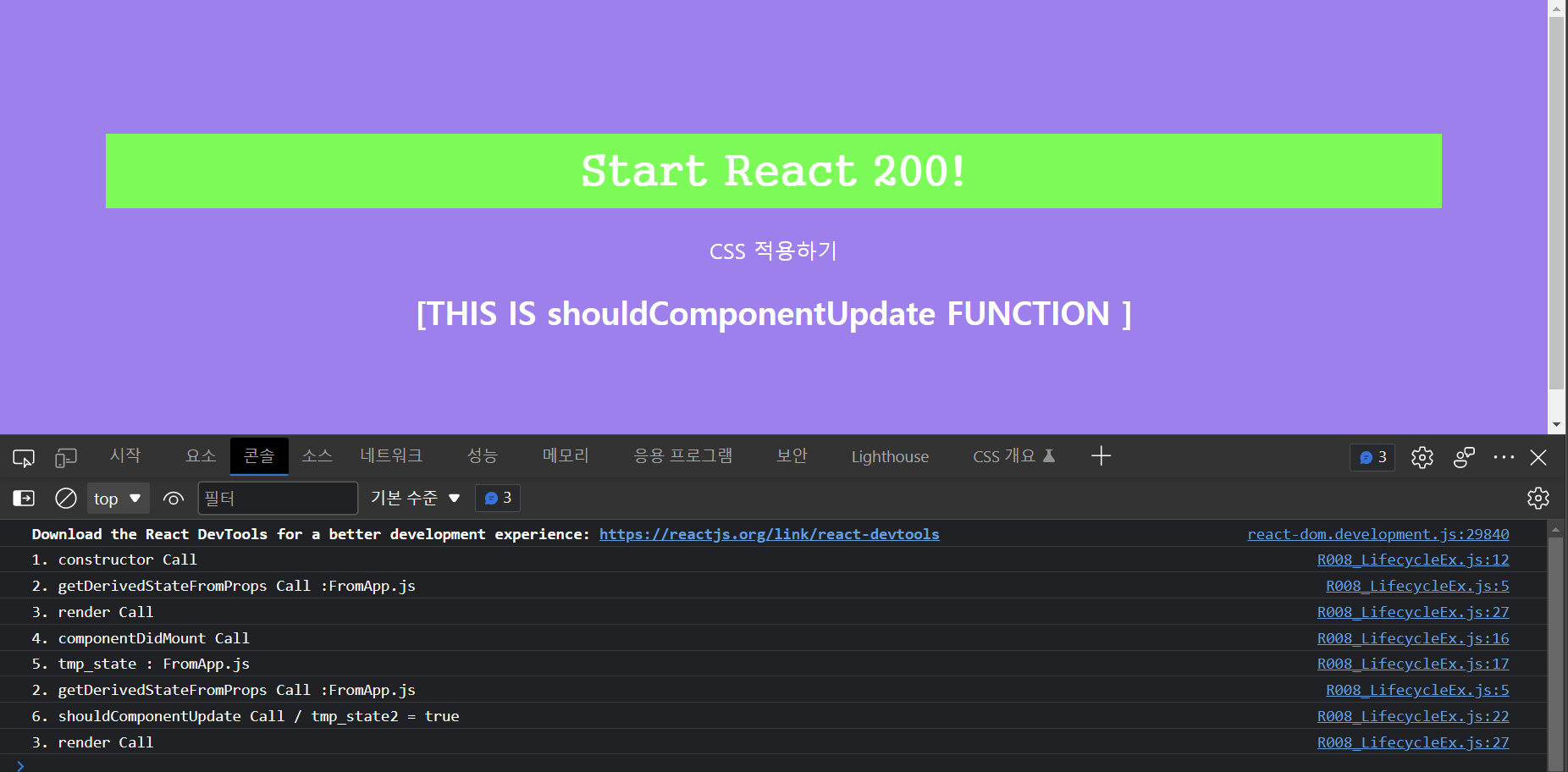
setState() 함수는 변수의 선언과 초기화를 동시에 실행합니다.
이 함수를 통해 state의 변경이 발생했기 때문에, '변경' 단계의 생명 주기 함수 shouldComponentUpdate()가 실행됩니다. return 값이 true(tmp_state2)이므로 render() 함수도 재실행됩니다.

'프론트엔드' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [HTML] html class 속성과 id 속성의 차이점 (0) | 2023.03.27 |
|---|---|
| [HTML] HTML 태그 정리(div, span, img, input, a) (0) | 2023.03.27 |
| [HTML] HTML, DOM이란? (Hypertext Markup Language, DOM) (0) | 2023.03.27 |
| 인터넷/웹 1.0/브라우저 란? (0) | 2023.03.27 |
| Web 관련 핵심 키워드 정리(URL/URI, www, http/https) (1) | 2023.03.27 |



